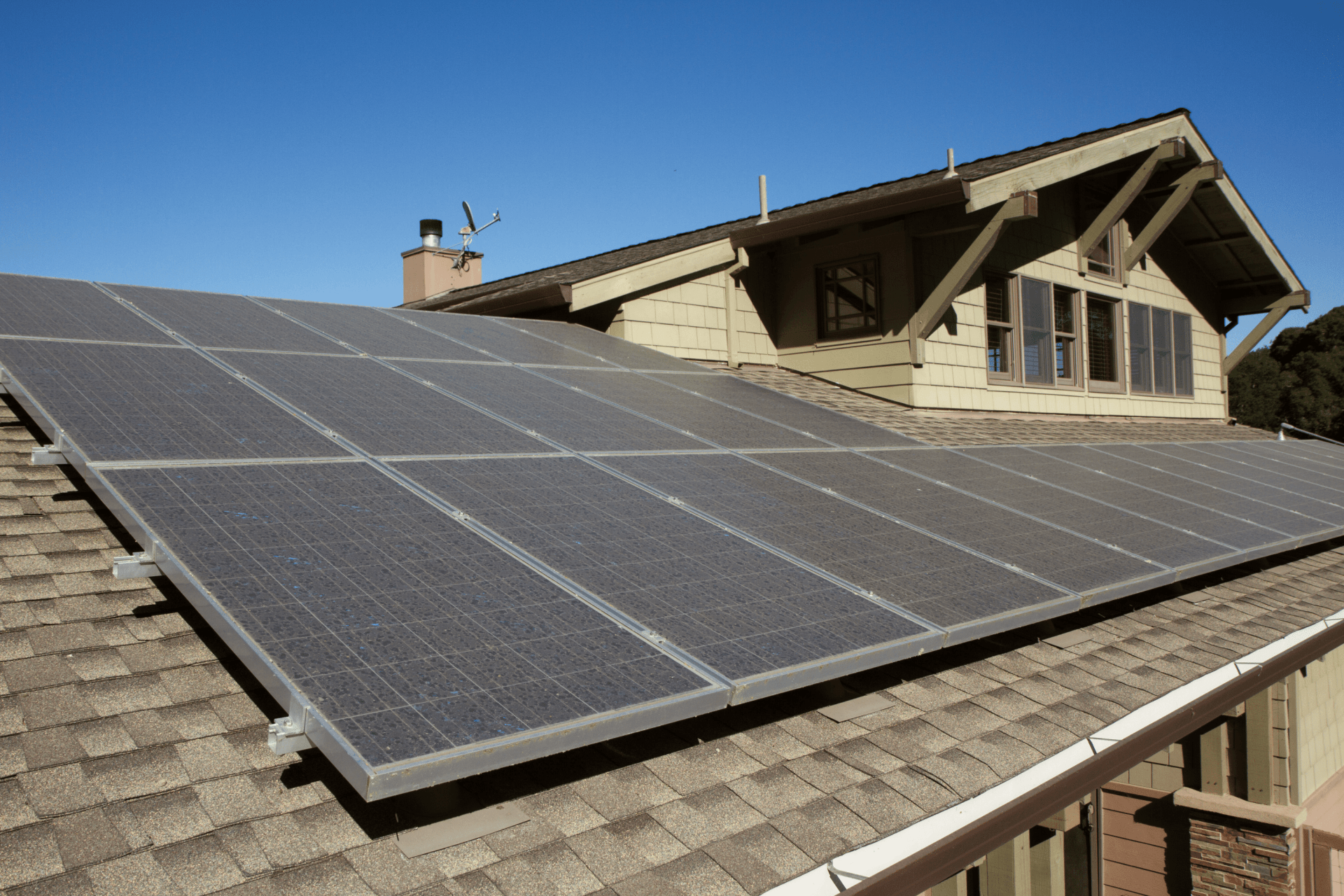
The Cost and Savings of installing Solar Panels, What to Expect
Considering installing solar panels but unsure about the costs and savings involved?
Our guide will walk you through the long-term savings of solar energy and help you estimate your potential savings.
Learn about upfront costs, tax credits, and incentives to calculate your monthly electric bill savings and payback period.
Explore factors affecting solar panel installation costs, tax breaks, incentives, and understand how various factors influence your savings.
Stay tuned for expert advice and insights on the worth of solar panels and other energy-saving guides.
Understanding the Cost and Savings of Installing Solar Panels
Understanding the cost and savings of installing solar panels involves analyzing the initial investment, potential savings on energy costs, and available tax credits and incentives.
One of the significant benefits of investing in solar panels is the long-term savings they offer. While the initial upfront costs may seem substantial, over time, solar panels can drastically reduce your electricity bills, leading to considerable savings. Solar panels are highly energy-efficient, tapping into a renewable source of energy that is abundant and sustainable. Harnessing solar power not only reduces your dependence on traditional fossil fuels but also decreases your carbon footprint, contributing to a greener environment.
Long-term solar savings
Long-term solar savings are achieved through the consistent production of electricity by solar panels, resulting in reduced average monthly energy bills over the years.
This steady electricity production enables households and businesses to significantly slash their reliance on traditional grid power, translating into notable annual savings. The upfront investment in solar panels pays off gradually as they continue to generate power with minimal maintenance costs, driving down the overall cost of electricity consumption. Over time, the sustainable power generation capacity of solar panels not only reduces the carbon footprint but also hedges against future electricity price hikes, making them a valuable long-term investment for cost-conscious individuals and environmentally conscious organizations.
How to estimate your solar savings
Estimating your solar savings involves calculating the initial investment, potential savings over time, and the overall efficiency of the solar panel system.
To start, determine the upfront cost of purchasing and installing solar panels, taking into account factors like the size of your system, location, available incentives, and installer fees.
Next, look at the potential savings you can generate by analyzing your current energy consumption, local electricity rates, and any applicable net metering policies.
Consider the long-term benefits of solar, such as reduced utility bills, protection against rising energy costs, and potential tax credits or rebates. Factor in the lifespan of the solar panels, maintenance costs, and any financing options available to assess the overall economic viability of the investment.
Find out your upfront costs
Determining your upfront costs for solar panel installation involves calculating the expenses associated with purchasing and installing the system in your home.Subtract tax credits (and other incentives)
After determining upfront costs, subtract available tax credits and incentives to evaluate the net savings and effective rate of return on your solar panel investment.Calculating Your Monthly Electric Bill Savings
Calculating your monthly electric bill savings with solar panels involves estimating the energy generated, usage patterns, and the resultant reduction in electricity costs.When determining the energy generated by solar panels, factors like the panel's efficiency, location, and the amount of sunlight it receives play a crucial role.
Understanding your usage patterns is essential; evaluate when you consume the most electricity and align it with solar production peaks for maximum savings.
The reduction in electricity bills is a direct result of using solar power to offset your consumption from the grid, reducing reliance on traditional utility providers.
Estimating these components collectively allows you to project your monthly savings and make informed decisions about transitioning to solar energy.
Calculating Your Payback Period
Calculating your payback period for solar panels involves evaluating the initial investment against the energy savings generated over time to determine the break-even point.Generally, the payback period is calculated by dividing the total upfront cost of installing solar panels by the annual energy cost savings the system generates. This analysis helps homeowners and businesses understand the timeframe required to recover their initial expense through reduced electricity bills. The shorter the payback period, the quicker the return on investment. Solar panel investments are not only environmentally friendly but also financially savvy, yielding long-term benefits both in cost savings and sustainable energy usage.
Estimating Your Solar Savings
Estimating your solar savings requires assessing the energy production capacity of the system, potential electricity bill reductions, and the overall efficiency of the solar power setup.
When considering the energy production capacity, factors like the size and orientation of your solar panels play a crucial role. System efficiency is determined by the quality of the components used and the maintenance of the system. To calculate potential electricity bill savings accurately, one must analyze historical consumption data and local utility rates. Understanding the power generation capacity of your system involves evaluating sunlight exposure, shading, and the tilt of the panels.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Installation Costs
Several factors influence solar panel installation costs, including the size of the system, home structure, location, and the type of panels selected for installation.
The size of the solar system plays a crucial role in determining the overall cost. Larger systems tend to be more expensive due to the increased number of panels and associated components required. Structural considerations are also vital, as homes with complex roofs or limited space may necessitate additional mounting equipment, impacting costs. Geographical location is significant, with sunny regions often offering better solar potential, translating to more efficient systems and lower long-term expenses. The type of panels chosen can vary in price and efficiency, ranging from monocrystalline to polycrystalline or thin-film options.
Exploring Tax Breaks and Incentives
Exploring tax breaks and incentives for solar panels involves researching federal and state-level programs that offer financial credits, rebates, or incentives for renewable energy investments.
One of the significant aspects of these programs is the federal investment tax credit (ITC) , which allows homeowners and businesses to deduct a percentage of the cost of installing a solar energy system from their federal taxes. This tax credit has played a pivotal role in making solar energy more affordable and accessible for many individuals. Various states offer their own rebates and incentives to further reduce the upfront costs associated with installing solar panels.
Understanding the Influence of Various Factors on Savings
Understanding how various factors influence savings from solar panels requires analyzing aspects such as energy consumption patterns, system efficiency, and external factors like weather conditions.In terms of energy consumption patterns , households or businesses with higher overall energy usage stand to benefit more from solar panels as they have greater potential for offsetting electricity bills. On the other hand, focusing on system efficiency is crucial, ensuring that the solar panel system is properly sized and maintained to maximize energy production.
Moreover, external factors such as geographical location and shading play a significant role in the overall savings. Areas with abundant sunlight yield higher energy generation, thereby increasing the financial benefits of solar panels. By considering all these factors comprehensively, individuals can make informed decisions about investing in solar energy for long-term savings and environmental benefits.
Locating State-specific Solar Incentives
Locating state-specific solar incentives involves consulting resources like the Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency to identify available savings programs, tax credits, and financial incentives for solar panel installations.State-specific solar incentives play a crucial role in the financial aspect of solar projects, making it essential to thoroughly research and understand the options available. One effective way to gather comprehensive information about solar incentives in a particular state is to explore official government websites related to energy or solar energy departments. These websites often offer detailed breakdowns of available financial aids, rebates, grants, and other incentives that can significantly reduce the cost of installing solar panels.
Seeking guidance from local solar energy organizations or professionals can provide valuable insights into the specific incentives and savings opportunities that are most relevant to a particular region. These experts can offer tailored advice based on the unique characteristics of the area, such as climate conditions, local regulations, and utility rates, to maximize the benefits of solar investments.
Assessing the Worth of Solar Panels
Assessing the worth of solar panels involves evaluating the investment returns, environmental benefits, and long-term savings potential for residential energy consumers.When considering the financial aspect, it's crucial to calculate the payback period and the overall return on investment (ROI) that solar panels can offer. The initial cost of installing solar panels may seem high, but over time, reduced utility bills and potential incentives can significantly offset these costs.
From an environmental standpoint, solar panels are known for their renewable energy production, which helps reduce carbon emissions and reliance on non-renewable energy sources. This shift towards cleaner energy contributes to a more sustainable future for all.
Residential users benefit from increased energy independence and security. By generating their electricity, homeowners can hedge against rising utility prices and unexpected power outages, providing peace of mind and control over their energy usage.
Is it worth paying off solar panels?
Determining if it's worth paying off solar panels involves assessing the initial investment, potential savings and the overall return on investment over time.When evaluating the financial implications of paying off solar panels, it's essential to factor in the upfront costs of purchasing and installing the solar system. This includes the price of the panels, inverters, mounting equipment, and any additional accessories needed for the setup.
One must consider the potential savings generated from reduced electricity bills. Solar panels have the ability to significantly lower your monthly energy expenses by leveraging the capabilities of the sun to generate clean, renewable energy.
Over time, these savings can accumulate, ultimately affecting the overall return on investment. It's crucial to analyze how long it would take for the energy savings to offset the initial investment in solar panels and begin yielding a positive return.
What are the main disadvantages of solar energy?
Identifying the main disadvantages of solar energy entails recognizing challenges such as high upfront costs, intermittent power generation, and dependency on weather conditions.
One of the primary drawbacks of solar energy lies in the significant initial investment required for the installation of solar panels and related infrastructure. This high upfront cost can deter many individuals and businesses from adopting solar energy solutions, as the financial outlay may not be feasible for everyone.
The intermittent nature of solar power generation poses a reliability concern, as energy production fluctuates depending on factors like sunlight availability and cloud cover. The dependency on weather conditions introduces a level of unpredictability, making it challenging to rely solely on solar energy for continuous power supply.
Guides from Solar Installers
Guides from solar installers offer expert advice on the installation, maintenance, and optimization of solar panel systems for residential and commercial applications.Installing solar panels involves specific steps that should be followed to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Guidance from experienced professionals can help in selecting the right location for solar panels, positioning them to receive maximum sunlight exposure, and ensuring proper wiring for effective energy production.
Maintenance procedures are essential to prolong the lifespan of solar systems. Regular cleaning of panels, checking for any obstructions to sunlight, and inspecting for any damages or malfunctions are crucial tasks that need to be done periodically.
Optimization techniques such as monitoring energy production, adjusting panel angles according to seasons, and investing in energy storage solutions can further enhance the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar systems.
Other Guides for Energy Saving
Apart from solar panels, there are various guides available for energy-saving practices, efficiency improvements, and sustainable solutions to reduce consumption and costs in residential and commercial settings.
One crucial aspect to consider is the implementation of energy-efficient appliances . Upgrading to appliances that are Energy Star certified can significantly reduce energy usage without sacrificing performance.
Another strategy is enhancing insulation in buildings to prevent heat loss during colder months, resulting in lower heating bills. Utilizing smart thermostats and programmable timers can help optimize energy usage according to specific needs and schedules, contributing to long-term savings.
There are also renewable energy options like wind turbines and geothermal systems that offer alternative ways to power homes and businesses sustainably while reducing reliance on traditional electricity sources.
Expert Advice and Insights
Seeking expert advice and insights on solar panels can provide valuable tips on system selection, installation best practices, and leveraging federal tax credits to maximize savings.
A knowledgeable solar panel expert can guide you through the various options available, taking into account your specific energy needs and budget constraints. They can recommend the most efficient and cost-effective system that aligns with your goals.
In terms of installation, experts can ensure that the panels are placed in optimal positions to harness maximum sunlight, enhancing the overall performance of your system.
Tapping into federal tax incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs of solar panel installation. Professionals can advise on the eligibility criteria and help you navigate the complex process of claiming these credits.
You might also like
Blog



Book a Service Today
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later
Request a Quote
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
Want to Learn More about Solar?
An In-Depth Look on Solar Companies in Fresno
 Get a Quote
Get a QuoteHarnessing the Sun's Power in Fresno: A Guide to Solar Energy
In Fresno, the shift towards sustainable and cost-effective solar energy is more than just a trend—it's a movement. Solar panels, or photovoltaic (PV) panels, are at the forefront of this change, transforming sunlight into electricity using semiconductor materials. This guide aims to shed light on the advantages of solar energy, the process of installing solar panels, and how they can significantly impact both your wallet and the environment positively.
Why Go Solar?
Opting for solar energy means tapping into an infinite and naturally renewing resource—the sun. This choice allows homeowners and businesses alike to cut down on fossil fuel usage, diminish their carbon footprint, and foster a more sustainable future. Beyond environmental benefits, solar panels promise substantial savings on electricity bills by enabling you to produce your own power, reducing reliance on the traditional electricity grid.
The Environmental and Economic Benefits
Solar energy stands out for its minimal environmental impact. It produces no greenhouse gas emissions or pollutants, making it a clean alternative to traditional energy sources. Moreover, solar panel installation offers an excellent return on investment through significant savings on energy expenses and potential increases in property value.
Understanding Solar Panel Installation
Before diving into solar energy, several considerations are crucial, such as your property's location, roof condition, and energy needs. The installation process involves consultation, design, permitting, actual panel installation, and connection to the power grid, with each step carefully planned to ensure efficiency and success.
Financing Your Solar Journey
The cost of solar installation varies, but federal and state incentives, along with tax credits, can help offset expenses. Various financing options, including solar loans and leasing, make going solar accessible and affordable. Moreover, maintaining and monitoring your system ensures it performs optimally over time, maximizing your investment.
Choosing the Right Solar Partner
Selecting a reputable solar installation company is essential. It's advisable to research, read reviews, request quotes, and verify the company's licensing and certifications. This diligence will lead you to a trustworthy partner for your solar energy journey.
Solar Energy in Fresno: A Bright Choice
Embracing solar energy in Fresno means joining a growing community focused on reducing energy costs and supporting environmental sustainability. With the city's ample sunny days, solar panel installation is not just feasible but highly beneficial, offering a cleaner, more cost-effective energy solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Transitioning to solar energy can raise many questions. Whether you're curious about the benefits, the types of solar options available, incentives, or specific services like battery storage, we're here to provide the answers. Our goal is to ensure you have all the information you need to make an informed decision about adopting solar energy.
Ready to Explore More?
Diving into the world of solar energy can be both exciting and overwhelming. We're here to guide you every step of the way—from understanding the basics of solar panels to navigating the installation process and maximizing your investment. If you're looking for a sustainable, cost-effective energy solution in Fresno, solar energy might just be the perfect fit.
For further details or to address any queries you might have, explore our Frequently Asked Questions section below. Here, you'll find insights into the advantages of going solar, available solar options, incentives, and more, helping you make an informed decision tailored to your needs and preferences.




Solar Fresno
When it comes to Solar, we know what's good!
The region's leading professional Solar Company





We're available
- Mon - Wed
- -
- Thu - Sat
- -
- Sunday
- -
Proudly powered by Snapps website builder
Disclaimer: This is a Referral Site, all sales and transactions are processed by Stockdale Solar LLC

